Get the case study as a PDF.
Reliable Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 T-cell Response with MHC I Dextramer®
Background
In this study, the epitope-specific T-cell responses were investigated in a cohort of COVID-19 recovered patients using a selected panel of SARS-CoV-2 specific MHC I Dextramer® reagents. The patient’s cohort presented asymptomatic to severe COVID-19 infections.
Study Description
A panel of nine different SARS-CoV-2 epitopes recently identified as potential targets for a CD8+ T-cell response to SARS-CoV-2 was chosen for this study. Blood from a cohort of 106 recovered COVID-19 patients (all HLA-A*0201 positive) was analyzed for CD8+ T cells reactivity against these nine different SARS-CoV-2 epitopes using MHC I Dextramer® reagents and flow cytometry.
Results
90% of the recovered COVID-19 patients mounted a detectable SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T-cell response to at least one, and up to seven, of the nine epitopes (Table 1, Fig. 1). The frequency of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD8+ T-cells was similar across all nine HLA-A2+ epitopes tested, with the highest individual responses observed for epitopes 3 and 6 (Fig.2). The cumulative frequency of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD8+ T cells across disease severity groups did not reveal any significant difference.
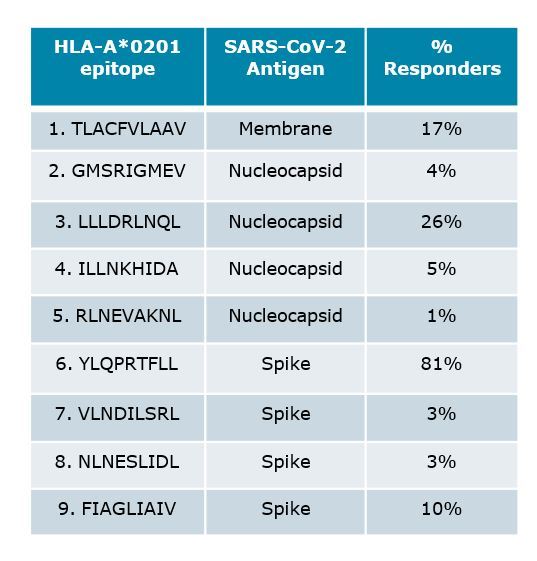
Table 1 The nine SARS-CoV-2 epitopes sequence, antigen and % positive responders.

Fig. 1 Example of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells identification in blood from a COVID-19 patient using HLA-A*0201 / YLQPRTFLL MHC I Dextramer®.

Fig. 2 Frequency of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD8+ T cells in the 106 HLA-A2+ individuals analyzed with the SARS-CoV-2 specific MHC I Dextramer® reagents.
Conclusions
- CD8+ T cells reactivity against SARS-CoV-2 plays a central role in the recovery of COVID-19 diseases
- 90% of the investigated individuals had a detectable SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T-cell response
- “The panel of Dextramer® applied here provides a new and sensitive representation of the general CD8+ T-cell response to SARS-CoV-2. It will be an important tool in assessing long-term immunity following infection or vaccination”

